Overview
Kubernetes 클러스터에서 외부로부터 들어오는 요청의 Source IP(클라이언트 IP) 를 정확히 파악하는 것은 로깅, 보안 분석, 감시(Audit), 접근 제어 등 다양한 운영 및 보안 목적에서 매우 중요하다.
그러나 Kubernetes의 기본 네트워크 구성에서는 서비스 타입에 따라 요청이 kube-proxy, NAT, ingress proxy 등을 거치며 Source IP가 변경되거나 소실되는 경우가 발생한다.
이 글에서는 Kubernetes 환경에서 Source IP가 왜 사라지는지, 그리고 이를 보존하기 위해 어떤 설정을 적용해야 하는지를 Service 타입별, Ingress 방식별로 정리한다.
또한 실습을 통해 실제 요청 시 IP가 어떻게 보이는지, 어떻게 보존할 수 있는지를 확인하는 과정을 Flask 앱과 MetalLB + Ingress-NGINX 조합을 이용한 실습을 통해 다룬다.
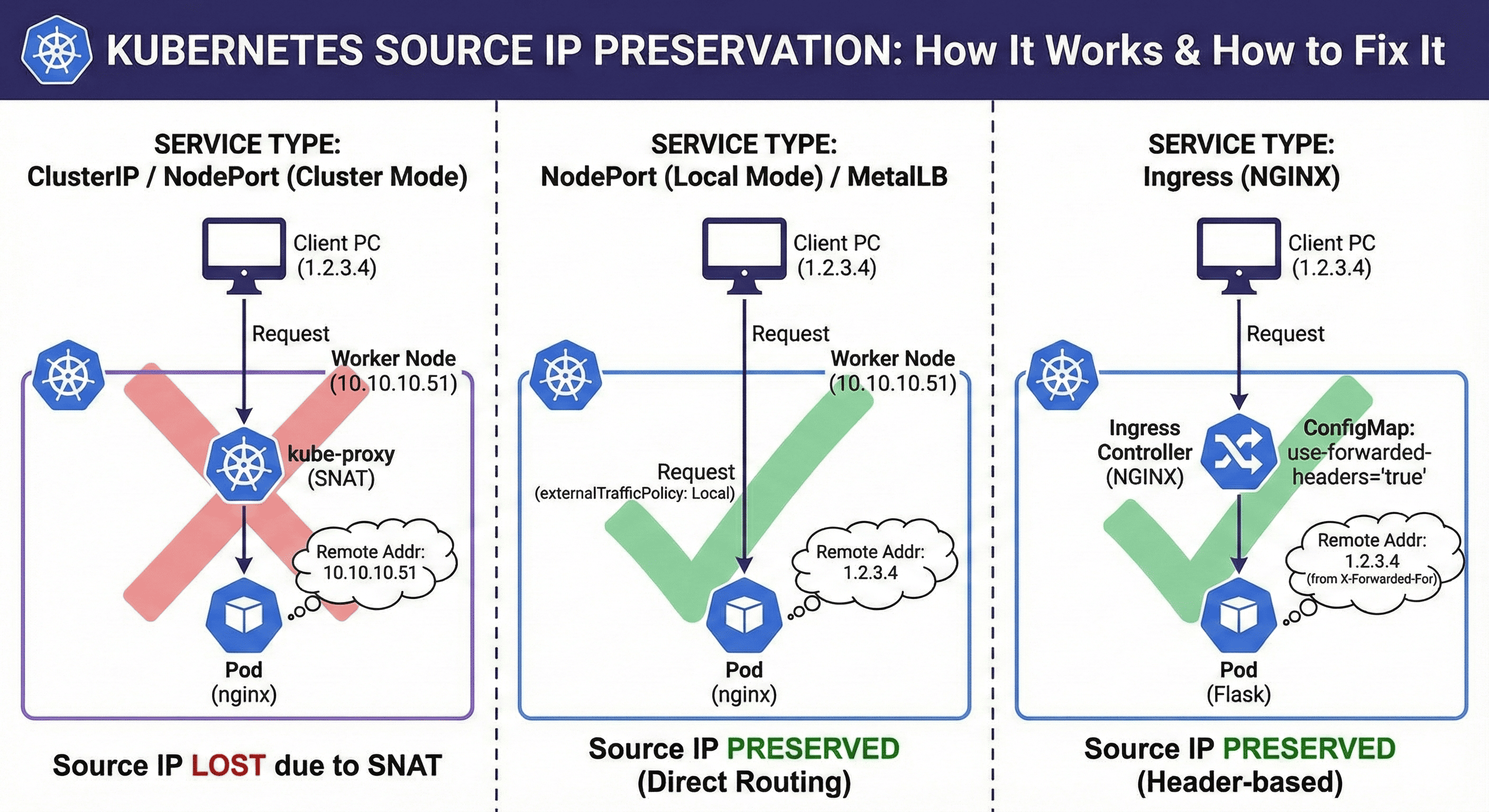
Service 타입별 Source IP 보존 여부
| 서비스 타입 | 설정 필요 여부 | 요청 전달 방식 | Source IP 보존 |
| ClusterIP | 불가능 | 클러스터 내부 kube-proxy 통해 전달 | ❌ |
| NodePort / LoadBalancer | externalTrafficPolicy: Local 설정 필요 | 클라이언트 → 노드 IP:포트 → 파드 직접 연결 | ✅ |
| Ingress | X-Forwarded-For 헤더 사용 필요 | 클라이언트 → Ingress Controller → 파드 | ✅ (헤더 기반) |
| MetalLB (LoadBalancer) | externalTrafficPolicy: Local 설정 필요 | 외부 IP → 직접 노드 라우팅 (L2/BGP) | ✅ |
- Ingress는 실제 IP가 파드까지 전달되지 않고, 헤더(X-Forwarded-For)로 전달되므로 애플리케이션에서 헤더 파싱이 필요하다.
왜 Cluster 모드에서는 Source IP가 사라질까?
Cluster 모드는 kube-proxy가 iptables 또는 ipvs로 트래픽을 전달하면서 SNAT(Source NAT) 처리를 수행하기 때문에, 요청자의 IP 대신 노드의 IP가 기록된다.
Local 모드는 SNAT 없이 로컬 노드에 있는 파드로 직접 전달하기 때문에 원본 IP가 보존된다.
`externalTrafficPolicy: Local` 사용하기
LoadBalancer 또는 NodePort 서비스에 다음과 같이 설정하면 클라이언트의 원래 IP를 유지할 수 있다.
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: my-service
spec:
type: LoadBalancer
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
selector:
app: my-app
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080- `Local`: 클라이언트의 원래 IP가 보존된다.
- `Cluster`(기본값): 요청이 클러스터 내에서 NAT 처리되어 Source IP가 노드 IP로 바뀐다.
단, 해당 노드에 파드가 없으면 요청이 실패할 수 있으므로, DaemonSet 활용 또는 리소스 분산을 고려해야 한다.
Ingress(NGINX)에서 Source IP 보존하기
필수 조건 2가지
| 항목 | 설정 | 설명 |
| Service 설정 | `externalTrafficPolicy: Local` | 클라이언트 IP가 SNAT되지 않고 그대로 전달되도록 합니다. |
| ConfigMap 설정 | `use-forwarded-headers: "true"` `proxy-real-ip-cidr: "0.0.0.0/0"` |
전달받은 `X-Forwarded-For`, `X-Real-IP` 값을 신뢰해서 로그 및 백엔드로 넘긴다. |
Configmap 설정
Ingress 컨트롤러(NGINX 등)는 기본적으로 L7 Proxy로 동작하기 때문에 Source IP가 변경된다. 이를 보존하려면 다음과 같이 설정한다.
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress-controller
data:
use-forwarded-headers: "true"
proxy-real-ip-cidr: 0.0.0.0/0
| 키 | 설명 |
| `use-forwarded-headers: "true"` | `X-Forwarded-For`, `X-Real-IP` 등 HTTP 헤더를 신뢰하고 사용하겠다는 의미이다. |
| `proxy-real-ip-cidr: 0.0.0.0/0` | 어떤 클라이언트 IP든 신뢰하겠다는 의미입니다. 보통은 내부 네트워크 대역을 제한하는 게 보안상 좋다. 예: `10.0.0.0/8`, `192.168.0.0/16` 등. |
이 설정은 NGINX가 `$proxy_protocol_addr`, `$remote_addr` 등을 올바르게 파싱할 수 있도록 해준다.
Service 설정
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: ingress-nginx-controller
namespace: ingress-nginx
spec:
type: LoadBalancer # 또는 NodePort
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: http
- port: 443
targetPort: https
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: ingress-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/component: controller
실습1: Source IP 확인 방법
1. flask 파드에 로그 설정 추가
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: flask-app
labels:
app: flask-app
spec:
containers:
- name: flask-app
image: python:3.9-slim
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8080"
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
pip install flask
mkdir -p /app
cp /config/app.py /app/
cd /app
python app.py
volumeMounts:
- name: flask-app-config
mountPath: /config
volumes:
- name: flask-app-config
configMap:
name: flask-app-config
2. Service 설정
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: flask-app-service
spec:
type: NodePort
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
selector:
app: flask-app
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
3. Configmap 설정
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: flask-app-config
data:
app.py: |
from flask import Flask, request
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
client_ip = request.remote_addr
x_forwarded_for = request.headers.get('X-Forwarded-For', '')
x_real_ip = request.headers.get('X-Real-IP', '')
all_headers = dict(request.headers)
response = f"""
Hello from Flask!
Client Info:
------------
Remote Addr: {client_ip}
X-Forwarded-For: {x_forwarded_for}
X-Real-IP: {x_real_ip}
All Request Headers:
-------------------
{all_headers}
"""
return response
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=int(os.environ.get('PORT', 8080)))
ConfigMap 적용 포함한 Flask Pod + Service + ConfigMap 전체 구성
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: flask-app-config
data:
app.py: |
from flask import Flask, request
import os
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello():
client_ip = request.remote_addr
x_forwarded_for = request.headers.get('X-Forwarded-For', '')
x_real_ip = request.headers.get('X-Real-IP', '')
all_headers = dict(request.headers)
response = f"""
Hello from Flask!
Client Info:
------------
Remote Addr: {client_ip}
X-Forwarded-For: {x_forwarded_for}
X-Real-IP: {x_real_ip}
All Request Headers:
-------------------
{all_headers}
"""
return response
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run(host='0.0.0.0', port=int(os.environ.get('PORT', 8080)))
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: flask-app
labels:
app: flask-app
spec:
containers:
- name: flask-app
image: python:3.9-slim
ports:
- containerPort: 8080
env:
- name: PORT
value: "8080"
command: ["/bin/sh", "-c"]
args:
- |
pip install flask
mkdir -p /app
cp /config/app.py /app/
cd /app
python app.py
volumeMounts:
- name: flask-app-config
mountPath: /config
volumes:
- name: flask-app-config
configMap:
name: flask-app-config
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: flask-app-service
spec:
type: NodePort
externalTrafficPolicy: Local
selector:
app: flask-app
ports:
- port: 8080
targetPort: 8080
4. 외부에서 curl 요청
curl http://<NodeIP>:<NodePort>
5. 실습 확인
이제 확인해본다.
# 같은 대역대 예시
curl 10.10.10.51:30378
Hello from Flask!
Client Info:
------------
Remote Addr: 10.10.10.50
X-Forwarded-For:
X-Real-IP:
All Request Headers:
-------------------
{'Host': '10.10.10.51:30378', 'User-Agent': 'curl/7.81.0', 'Accept': '*/*'}
--------------------------------------------
# 다른 대역대 예시
curl 10.10.10.51:30378
Hello from Flask!
Client Info:
------------
Remote Addr: 10.10.10.251
X-Forwarded-For:
X-Real-IP:
All Request Headers:
현재 상황 요약
- `externalTrafficPolicy: Local` 설정
- `NodePort` 로 워커 노드에 직접 접속
- FLASK 응답에 `$remote_addr` 는 보이고 같은 대역대에서는 source ip를 잘 보존한다. 다른 대역대에서는 실제 외부 IP가 아닌 게이트웨이 IP (예: 10.10.10.251) 로 나타남 ❌
원인: kube-proxy + NAT + Gateway ( 다른 대역대)
당신이 요청을 보낼 때, 요청이 물리적인 라우터 또는 가상 게이트웨이를 거쳐 오기 때문에 flask 파드에서는 실제 외부 클라이언트 IP가 아니라 게이트웨이 또는 NAT IP를 보게 된다.
[Your MacBook]
↓ (요청)
[GW or NAT (10.10.10.251)]
↓ (SNAT됨)
[Worker Node (10.10.10.51):32440]
↓
[nginx Pod]- 결국 FLASK는 직접적인 클라이언트 IP가 아니라 SNAT된 IP (게이트웨이 IP) 를 받게 된다.
실습 2: MetalLB + Ingress-NGINX로 Source IP 보존
1. Metal LB 설정
Metal LB를 설치해준 뒤 진행해야 한다.
k get ipaddresspools.metallb.io -n metallb
NAME AUTO ASSIGN AVOID BUGGY IPS ADDRESSES
ip-pool true false ["10.10.10.55-10.10.10.58","10.10.10.62-10.10.10.65"]
2. Ingress-NGINX Controller 설정
Test Ingress Nginx Controller를 Helm으로 생성해준다.
global:
image:
# -- Registry host to pull images from.
registry: registry.k8s.io
controller:
ingressClassResource:
name: nginx-test # 구분을 위한 새로운 이름
enabled: true
default: false # 기본 컨트롤러가 아님을 명시
controllerValue: "k8s.io/ingress-nginx-test" # 구분을 위한 새로운 controller 값
service:
# -- Enable controller services or not. This does not influence the creation of either the admission webhook or the metrics service.
enabled: true
type: LoadBalancer
loadBalancerIP: "10.10.10.63"
externalTrafficPolicy: "Local"
config:
use-forwarded-headers: "true"
real-ip-header: "X-Forwarded-For"
set-real-ip-from: "0.0.0.0/0"
real-ip-recursive: "true"
설치를 진행해준다.
helm install ingress-nginx-test . -n ingress-nginx -f ./values/mgmt-test.yaml
확인한다.
k get svc -n ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-test-controller -o yaml | grep external
externalTrafficPolicy: Localk get cm -n ingress-nginx ingress-nginx-test-controller -o yaml
apiVersion: v1
data:
proxy-real-ip-cidr: 0.0.0.0/0
use-forwarded-headers: "true"
..
3. nginx test.yaml 작성
apiVersion: v1
kind: ConfigMap
metadata:
name: nginx-config
namespace: default
data:
nginx.conf: |
events {}
http {
log_format main '$http_x_forwarded_for - $remote_user [$time_local] "$request" '
'$status $body_bytes_sent "$http_referer" '
'"$http_user_agent" "$http_x_forwarded_for"';
access_log /var/log/nginx/access.log main;
set_real_ip_from 0.0.0.0/0;
real_ip_header X-Forwarded-For;
real_ip_recursive on;
server {
listen 80;
location / {
return 200 'Hello from NGINX!';
}
}
}
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:latest
ports:
- containerPort: 80
volumeMounts:
- name: config
mountPath: /etc/nginx/nginx.conf
subPath: nginx.conf
volumes:
- name: config
configMap:
name: nginx-config
---
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: nginx-service
spec:
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 80
---
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: nginx-ingress
spec:
ingressClassName: nginx-test
rules:
- host: test.local
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: Prefix
backend:
service:
name: nginx-service
port:
number: 80
4. 테스트 방법
`/etc/hosts` 에 `test.local` 등록 (로컬 환경이라면)
echo "<LoadBalancer-IP> test.local" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
# 나의 경우
echo "10.10.10.63 test.local" | sudo tee -a /etc/hosts
접속 테스트
테스트 해본다.
# 외부망
curl http://test.local
Hello from Nginx!
Remote Addr: 10.233.65.165
X-Forwarded-For: 10.10.10.251
# 내부망
curl http://test.local
Hello from Nginx!
Remote Addr: 10.233.65.165
X-Forwarded-For: 10.10.10.60
curl 요청 시 -H "X-Forwarded-For: 1.2.3.4" 직접 지정해서 확인해본다.
curl -H "Host: test.local" -H "X-Forwarded-For: 1.2.3.4" http://10.10.10.63
nginx 로그에 1.2.3.4가 찍히면 nginx 파드가 real_ip_header 제대로 읽고 있다는 뜻이다.
결과는 아까 NodePort로 테스트 한것 과 동일하다.
마무리
Kubernetes에서 Source IP를 보존하는 것은 단순히 클라이언트 위치를 파악하기 위한 정보 수집 차원을 넘어,
보안 정책 수립, 공격자 추적, 서비스 최적화, 접근 제어, 트래픽 분석 등 다양한 운영 측면에서 필수적인 요소이다.
특히:
- externalTrafficPolicy: Local 은 Kubernetes 서비스에서 SNAT을 피하고 원본 IP를 보존할 수 있는 가장 핵심적인 설정이다.
- Ingress 환경에서는 X-Forwarded-For 와 real_ip_header 설정을 통해 간접적으로 원본 IP를 전달받을 수 있다.
- MetalLB, Cilium 등 L2/L3 수준에서 Source IP를 정확히 전달할 수 있는 인프라 구성도 병행되어야 한다.
실제 운영 환경에서는 DaemonSet을 활용한 파드 분산, IP 신뢰 범위 제한(CIDR 필터링), 보안 고려 등을 함께 설계해야 하며,
불필요한 SNAT 처리를 최소화하고 클라이언트 식별의 신뢰성을 확보하는 것이 중요하다.
Reference
'Container Orchestration > Kubernetes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 배포하다 서비스 터진 적 있다면? 꼭 알아야 할 Kubernetes 전략 가이드 (2) | 2025.05.28 |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes Endpoint와 EndpointSlice 완벽 정리 (0) | 2025.05.22 |
| Harbor SSO 구성 가이드(OIDC : Azrue AD, Gitlab) (0) | 2025.04.07 |
| Kubernetes Gateway API 완전 정복 (0) | 2025.04.04 |
| Kubernetes에 static-file-server 생성하기 (0) | 2025.03.24 |
