Overview
지난 시간에는 Helm의 개념과 주요 명령어에 대해 학습했다.
이번 글에서는 Helm Chart를 직접 작성하는 방법에 대해 알아보며, Helm을 실무에 적용하기 위한 기초 체력을 다져본다.
`helm create` 명령어로 생성된 기본 템플릿 구조를 살펴보고, values.yaml 값을 어떻게 활용해 템플릿과 결합되는지 실습을 통해 확인해본다.
또한 `--dry-run` 및 `--debug` 옵션을 활용한 배포 전 사전 점검 방법까지 다룬다.
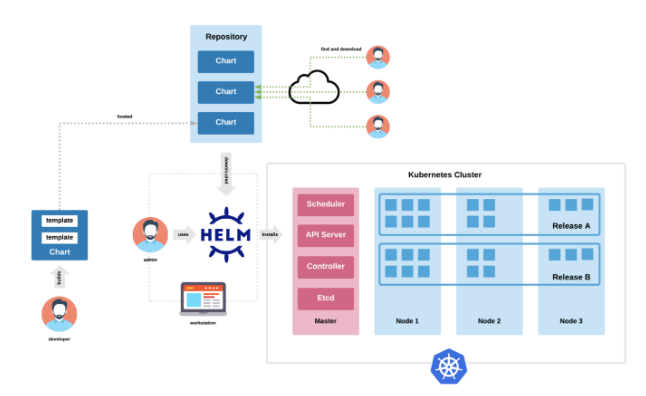
Helm Chart 구조에 대한 이해는 향후 Helm 기반의 마이크로서비스 배포 및 GitOps 전략 수립 시 필수적인 기초가 된다.
📅 관련 글
2022.09.06 - [Container Orchestration/Kubernetes] - Helm 이란? (Kubernetes Package manager)
2024.11.15 - [Container Orchestration/Kubernetes] - Helm Chart Template 문법
2024.12.20 - [Container Orchestration/Kubernetes] - Helm Chart 생성 및 패키징 (gh-pages)
2025.01.06 - [Container Orchestration/Kubernetes] - Helm Base App Chart 생성(With ArgoCD)
Helm Chart 작성방법
Helm CLI가 설치되어 있으면, `helm create` 명령을 실행하여 새로운 차트를 생성할 수 있다.
다음은 Helm Chart의 기본 구조이다.
$ helm create somaz
Creating somaz
$ tree somaz/
somaz/
├── Chart.yaml
├── charts
├── templates
│ ├── NOTES.txt
│ ├── _helpers.tpl
│ ├── deployment.yaml
│ ├── hpa.yaml
│ ├── ingress.yaml
│ ├── service.yaml
│ ├── serviceaccount.yaml
│ └── tests
│ └── test-connection.yaml
└── values.yaml
3 directories, 10 files- `bash_completion` 등록을 해본다. 리눅스 기준으로 작성한다.
공식사이트에 설명이 되어있다.
$ vi ~/.bashrc
# 맨 마지막에
sudo bash -c 'helm completion bash > /etc/bash_completion.d/helm'
Helm Chart Install
`-f` 옵션을 주고 overide.values.yaml을 사용하여 Install 할 수 있다.
helm install -f <오버라이딩 파일경로> <Release 이름> <차트경로>
ex)
helm install -f myvalues.yaml myredis ./redis
`helm install`(또는 `upgrade`)할 때 `--set` 을 사용하면 `values.yaml` 필드를 오버라이딩 할 수 있다.
helm install --set <오버라이딩 필드>=<값> <Release 이름> <차트경로>
ex)
helm install --set image=redis:latest myredis ./redis
위와 같이 작성하면 `image` 필드가 `redis:latest` 로 변경이 된다.
image: redis:stable -> image: redis:latest
Helm 값 병합 우선순위 정리
Helm에서는 여러 방식으로 값을 주입할 수 있는데, 같은 필드에 여러 값이 주어졌을 경우 우선순위에 따라 마지막 값으로 병합된다. 아래는 값 병합 시 우선순위 정리이다.
values.yaml < -f custom.yaml < --set key=value < --set-file즉, 기본 `values.yaml` 값이 가장 낮은 우선순위를 가지며, `-f` 로 넘긴 파일이 이를 덮어쓰고, `--set` 옵션은 그보다 더 우선한다. 마지막으로 `--set-file` 은 파일 내용을 직접 키에 바인딩하기 때문에 가장 높은 우선순위를 가진다.
이러한 병합 우선순위를 이해하고 있으면, Helm Chart 배포 시 환경별 설정 파일을 깔끔하게 관리할 수 있다.
Helm Chart 문법
먼저 Helm Chart의 주요 구성요소에 대해서 확인해보겠다.
helm 설치 후 `helm create` 명령어를 사용해 Sample Chart를 생성할 수 있다.
$ helm create somaz
$ cd somaz
$ ls
Chart.yaml charts templates values.yaml
$ ls templates/
NOTES.txt _helpers.tpl deployment.yaml hpa.yaml ingress.yaml service.yaml serviceaccount.yaml tests
Chart.yaml
차트 자체에 대한 메타데이터가 포함된 기본 파일이다. `name, version, description, home, keywords, sources,` 등과 같은 필드가 포함된다. dependencies는 `package.json`(Node.js에서) 또는 `pom.xml`(Maven에서)과 약간 비슷하다고 볼 수 있다.
values.yaml
차트의 기본 구성 값을 작성한다. 다양한 환경에 대해 다양한 값으로 템플릿을 매개변수화할 수 있는 곳이다.
해당 파일의 작성한 값들을 기준으로 template의 yaml 파일로 오버라이딩 된다.
templates
값과 결합될 때 유효한 Kubernetes 매니페스트 파일을 생성하는 템플릿의 디렉터리이다. 템플릿은 Go 템플릿 언어를 사용한다.
Helm Chart 작성 베스트 프랙티스
Helm Chart를 작성할 때는 다음과 같은 베스트 프랙티스를 따르는 것이 유지보수에 큰 도움이 된다.
1. `_helpers.tpl` 분리
공통적으로 사용되는 템플릿 함수(예: `fullname, labels, selectorLabels`)는 `_helpers.tpl` 파일에 정의하고 `include` 로 불러온다.
{{- define "myapp.fullname" -}}
{{- printf "%s-%s" .Release.Name .Chart.Name | trunc 63 | trimSuffix "-" -}}
{{- end -}}metadata:
name: {{ include "myapp.fullname" . }}
2. `include, define, template` 활용
템플릿 중복을 줄이고 재사용 가능하게 만듭니다. 특히 여러 리소스에 동일한 label이나 이름 규칙을 적용할 때 유용하다.
3. 필요한 템플릿만 생성하도록 조건부 생성 활용
{{- if .Values.service.enabled }} apiVersion: v1 kind: Service ... {{- end }}4. 템플릿 안에서 들여쓰기와 공백 관리
- `{{-` 또는 `-}}` 를 활용해 불필요한 공백 제거
- `nindent, indent` 함수로 YAML 들여쓰기 관리
labels:
{{- include "myapp.labels" . | nindent 4 }}5. 리소스별로 `values.yaml` 을 잘게 쪼개기
`service, deployment, ingress` 등을 나눠 명확한 구조를 갖도록 작성하면 환경별 override 도 훨씬 편해진다.
아래는 templates의 `deployment.yaml` 예시이다.
$ cat deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: {{ include "somaz.fullname" . }}
labels:
{{- include "somaz.labels" . | nindent 4 }}
spec:
{{- if not .Values.autoscaling.enabled }}
replicas: {{ .Values.replicaCount }}
{{- end }}
selector:
matchLabels:
{{- include "somaz.selectorLabels" . | nindent 6 }}
template:
metadata:
{{- with .Values.podAnnotations }}
annotations:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
labels:
{{- include "somaz.selectorLabels" . | nindent 8 }}
spec:
{{- with .Values.imagePullSecrets }}
imagePullSecrets:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
serviceAccountName: {{ include "somaz.serviceAccountName" . }}
securityContext:
{{- toYaml .Values.podSecurityContext | nindent 8 }}
containers:
- name: {{ .Chart.Name }}
securityContext:
{{- toYaml .Values.securityContext | nindent 12 }}
image: "{{ .Values.image.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.tag | default .Chart.AppVersion }}"
imagePullPolicy: {{ .Values.image.pullPolicy }}
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: {{ .Values.service.port }}
protocol: TCP
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: http
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: http
resources:
{{- toYaml .Values.resources | nindent 12 }}
{{- with .Values.nodeSelector }}
nodeSelector:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
{{- with .Values.affinity }}
affinity:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
{{- with .Values.tolerations }}
tolerations:
{{- toYaml . | nindent 8 }}
{{- end }}
간단히 문법에 대해서 설명해보자면,
조건절은 `{{- if }}` 혹은 `{{- if not }} {{ end }}` 로 사용할 수 있고
`{{- with 키 }} {{ end }}` 는 with 절 안에서는 구조상 해당 키 아래의 값들을 사용하겠다는 의미이다.
`{{- toYaml 키 }}` 는 키의 값을 그대로 Yaml 로 프린트해준다.
이제 간단히 실습을 진행해본다.
아래는 `values.yaml` 파일 예시이다.
$ cat values.yaml
# Default values for somaz.
# This is a YAML-formatted file.
# Declare variables to be passed into your templates.
replicaCount: 1
image:
repository: nginx
pullPolicy: IfNotPresent
# Overrides the image tag whose default is the chart appVersion.
tag: "latest"
imagePullSecrets: []
nameOverride: ""
fullnameOverride: "somaz-nginx"
serviceAccount:
# Specifies whether a service account should be created
create: true
# Annotations to add to the service account
annotations: {}
# The name of the service account to use.
# If not set and create is true, a name is generated using the fullname template
name: ""
podAnnotations: {}
podSecurityContext: {}
# fsGroup: 2000
securityContext: {}
# capabilities:
# drop:
# - ALL
# readOnlyRootFilesystem: true
# runAsNonRoot: true
# runAsUser: 1000
service:
type: ClusterIP
port: 80
ingress:
enabled: false
className: ""
annotations: {}
# kubernetes.io/ingress.class: nginx
# kubernetes.io/tls-acme: "true"
hosts:
- host: chart-example.local
paths:
- path: /
pathType: ImplementationSpecific
tls: []
# - secretName: chart-example-tls
# hosts:
# - chart-example.local
resources: {}
# We usually recommend not to specify default resources and to leave this as a conscious
# choice for the user. This also increases chances charts run on environments with little
# resources, such as Minikube. If you do want to specify resources, uncomment the following
# lines, adjust them as necessary, and remove the curly braces after 'resources:'.
# limits:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi
# requests:
# cpu: 100m
# memory: 128Mi
autoscaling:
enabled: false
minReplicas: 1
maxReplicas: 100
targetCPUUtilizationPercentage: 80
# targetMemoryUtilizationPercentage: 80
nodeSelector: {}
tolerations: []
affinity: {}
namespace: somaz- default로 주어지는 `sample values.yaml` 파일이다.
- 수정한 부분은 image tag와 밑에 `namespace : somaz` 만 추가해 주었다.
이제 간단하게 `--dry-run` 과 `--debug` 명령어를 사용해 helm chart 설치 결과가 어떻게 나오는지 확인해본다.
$ helm install -f values.yaml somaz-nginx . --dry-run --debug
install.go:200: [debug] Original chart version: ""
install.go:217: [debug] CHART PATH: /home/somaz/somaz
...
HOOKS:
---
# Source: somaz/templates/tests/test-connection.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: "somaz-nginx-test-connection"
labels:
helm.sh/chart: somaz-0.1.0
app.kubernetes.io/name: somaz
app.kubernetes.io/instance: somaz-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/version: "1.16.0"
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
annotations:
"helm.sh/hook": test
spec:
containers:
- name: wget
image: busybox
command: ['wget']
args: ['somaz-nginx:80']
restartPolicy: Never
MANIFEST:
---
# Source: somaz/templates/serviceaccount.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: somaz-nginx
labels:
helm.sh/chart: somaz-0.1.0
app.kubernetes.io/name: somaz
app.kubernetes.io/instance: somaz-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/version: "1.16.0"
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
---
# Source: somaz/templates/service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: somaz-nginx
labels:
helm.sh/chart: somaz-0.1.0
app.kubernetes.io/name: somaz
app.kubernetes.io/instance: somaz-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/version: "1.16.0"
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
spec:
type: ClusterIP
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: http
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app.kubernetes.io/name: somaz
app.kubernetes.io/instance: somaz-nginx
---
# Source: somaz/templates/deployment.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: somaz-nginx
labels:
helm.sh/chart: somaz-0.1.0
app.kubernetes.io/name: somaz
app.kubernetes.io/instance: somaz-nginx
app.kubernetes.io/version: "1.16.0"
app.kubernetes.io/managed-by: Helm
spec:
replicas: 1
selector:
matchLabels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: somaz
app.kubernetes.io/instance: somaz-nginx
template:
metadata:
labels:
app.kubernetes.io/name: somaz
app.kubernetes.io/instance: somaz-nginx
spec:
serviceAccountName: somaz-nginx
securityContext:
{}
containers:
- name: somaz
securityContext:
{}
image: "nginx:latest"
imagePullPolicy: IfNotPresent
ports:
- name: http
containerPort: 80
protocol: TCP
livenessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: http
readinessProbe:
httpGet:
path: /
port: http
resources:
{}
...
Helm Template 디버깅 Best Practice
실무에서 Helm Template 작성 시 가장 흔한 오류는 다음과 같다.
- .Values.key 가 존재하지 않아 nil 에러 발생
- 중첩된 구조의 key 오타
- 조건문/반복문 내 들여쓰기 오류
- 함수 사용 시 괄호 누락
이런 오류를 미리 방지하려면 Helm에서 제공하는 함수들을 잘 활용하는 것이 중요하다.
| 함수 | 설명 | 예시 |
| default | 기본값 설정 | `{{ default "nginx" .Values.image.repository }}` |
| required | 값이 없으면 오류 발생 | `{{ required "image.tag is required" .Values.image.tag }}` |
| printf | 포맷 문자열 출력 | `{{ printf "version-%s" .Chart.AppVersion }}` |
위 함수들을 적절히 활용하면 템플릿의 유효성 검사를 강화할 수 있다.
또한 `helm template` 또는 `helm install --dry-run --debug` 명령어로 실제 배포 전 결과 YAML을 미리 확인하는 습관은 필수입니이다. YAML 구조, 값 주입 상태, 들여쓰기 오류 등을 빠르게 파악할 수 있기 때문이다.
마무리: “직접 작성해보며 Helm Chart 구조를 내 것으로!”
Helm Chart는 단순히 템플릿으로 Kubernetes 리소스를 자동화하는 도구를 넘어,
팀의 배포 전략을 코드로 정의하고 재사용 가능하게 만드는 핵심 구성요소이다.
이번 실습을 통해 Helm Chart 디렉터리 구조, 템플릿 문법, values 값을 오버라이딩하는 다양한 방법을 이해할 수 있었다.
특히 `--dry-run, --debug` 옵션을 통해 사전 배포 점검을 하는 습관은 실무에서의 실수를 줄이고 배포 신뢰도를 높이는 데 큰 도움이 된다.
앞으로 다양한 환경별 Chart 구성을 다뤄보며 Helm의 확장성과 유연성을 더 깊이 있게 경험해보자.
차트 작성 능력을 갖추면, ArgoCD나 FluxCD와 같은 GitOps 도구와의 연동도 자연스럽게 이어질 것이다.
Reference
https://insight.infograb.net/blog/2022/03/14/gitlab-helm-package-registry/
https://devocean.sk.com/blog/techBoardDetail.do?ID=163262
'Container Orchestration > Kubernetes' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CertManager로 Let's Encrypt 인증서 발급 (2) | 2023.10.03 |
|---|---|
| Kubernetes Autoscaling & Karpenter (0) | 2023.05.24 |
| Helm 이란? (Kubernetes Package manager) (2) | 2023.05.16 |
| Kuberntes Service Account란? (0) | 2023.05.10 |
| Kubernetes Secret이란? (0) | 2023.05.09 |
